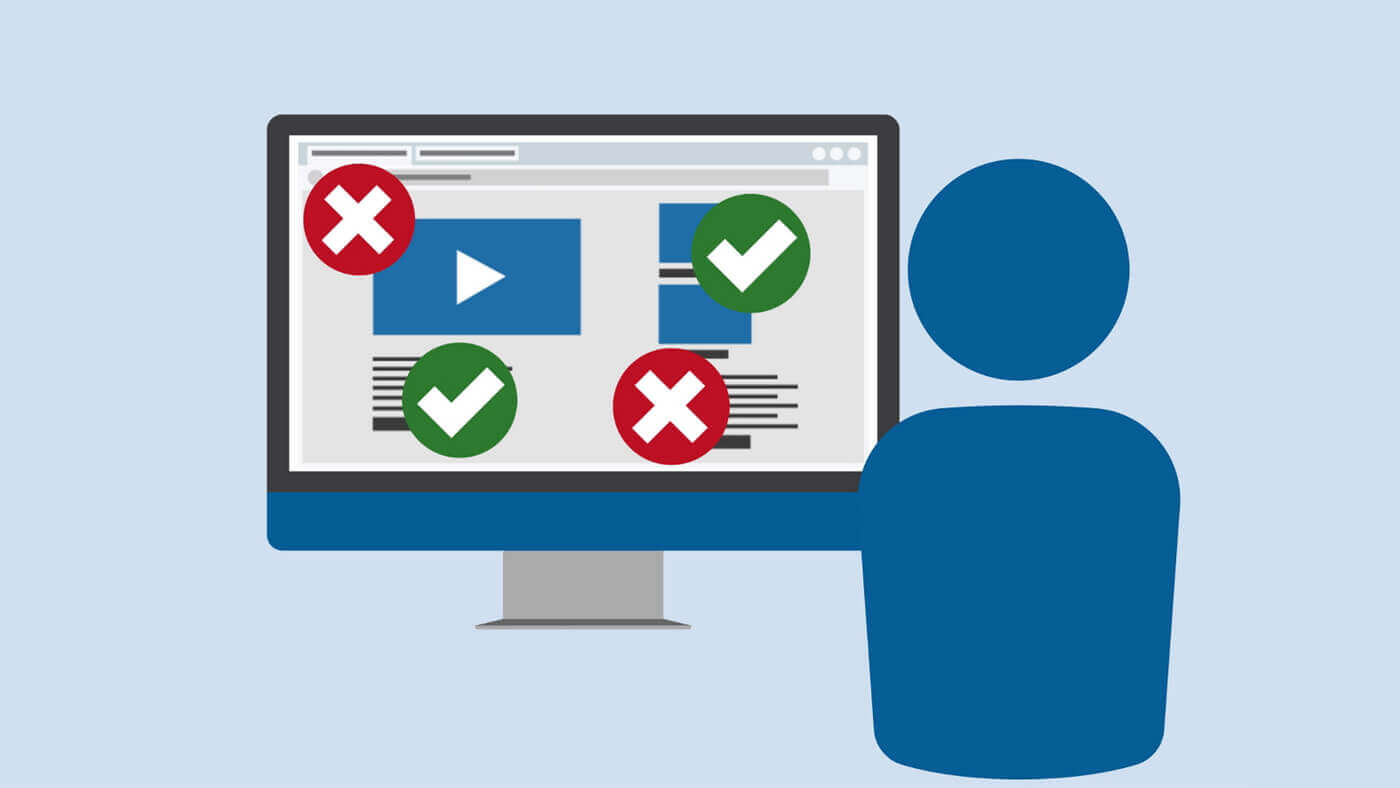
In the digital age, the internet serves as a gateway to information, services, and opportunities. However, not everyone can navigate this virtual landscape with the same ease. For individuals with disabilities, accessing websites can often be a frustrating and challenging experience due to barriers that hinder their ability to perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with web content.
Website accessibility, therefore, is not merely a matter of convenience but a fundamental right ensuring equal access to information and services for all. As we progress into 2024, the importance of making websites more accessible has become increasingly apparent.
In this guide, we’ll delve into what website accessibility entails, why it matters, and most importantly, how you can take practical steps to make your website more inclusive and accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities. Let’s embark on this journey toward creating a more inclusive digital space where everyone can participate fully and equally.
Table of Contents
What Is Website Accessibility?
Website accessibility refers to the practice of ensuring that websites are designed and developed in a way that makes them usable and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This means creating digital environments that can be navigated, understood, and interacted with by people with diverse abilities, including those who may have visual, auditory, motor, cognitive, or other impairments.

Accessible websites remove barriers that might otherwise prevent individuals with disabilities from accessing information, products, and services online. These barriers can include inaccessible design elements, such as images without alternative text for screen readers, videos without captions, poorly structured content that is difficult to navigate using assistive technologies, and more.
Website accessibility is not only about compliance with legal standards and guidelines but also about fostering inclusivity and equal participation in the digital realm. By prioritizing accessibility in web design and development, businesses and organizations can reach a broader audience, enhance user experience for all users, and demonstrate their commitment to diversity and inclusion.
Why Is Website Accessibility Important?
Website accessibility is paramount because it ensures inclusivity and equal access to information and services for individuals of all abilities. By adhering to accessibility standards and guidelines, websites become navigable and usable for those with disabilities, fostering a more inclusive digital environment.
Here are some of the key factors which make website accessiblity very important for your website users :-
Inclusivity and Equal Access
Ensuring website accessibility goes beyond mere compliance; it embodies a commitment to inclusivity and equal opportunity in the digital landscape. Imagine a visually impaired individual trying to access vital health information online, a person with motor impairments attempting to make an online purchase, or a deaf individual seeking to engage with video content—all of whom encounter barriers that hinder their ability to fully engage with the online world.

By prioritizing website accessibility, we empower these individuals to navigate websites independently, access information, and engage with online services effectively. This fosters a sense of empowerment and autonomy, allowing individuals with disabilities to participate more fully in education, employment, commerce, and social interactions online.
In essence, website accessibility is not merely about making adjustments to accommodate a specific group of users; it’s about creating a digital ecosystem where diversity is celebrated, barriers are dismantled, and everyone has an equal opportunity to thrive.
Legal Compliance
The legal landscape surrounding website accessibility underscores its importance as a fundamental aspect of digital governance and social responsibility. Laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States and the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) globally serve as robust frameworks for ensuring that websites are accessible to individuals with disabilities.

Non-compliance with these regulations not only risks legal repercussions, including lawsuits and fines but also undermines the principles of equality and inclusion. In recent years, there has been a notable increase in litigation related to website accessibility, with individuals and advocacy groups taking legal action against organizations whose websites fail to meet accessibility standards.
These legal challenges highlight the pressing need for businesses and organizations to prioritize accessibility in their digital strategies. By proactively adhering to accessibility guidelines and implementing best practices, entities can mitigate legal risks while also demonstrating their commitment to upholding the rights of individuals with disabilities.
Additionally, beyond legal considerations, embracing website accessibility reflects an organization’s ethical stance and dedication to creating a more equitable and inclusive online environment for all users.
Enhanced User Experience
The inclusive design principles that underpin website accessibility not only benefit individuals with disabilities but also enhance the user experience for all visitors. Clear navigation, descriptive images, and readable text are not just accommodations for specific user groups but essential elements of user-centric design that contribute to a seamless and intuitive browsing experience.

Clear navigation structures, for instance, facilitate easy exploration of website content, allowing users to locate information quickly and efficiently. This benefits not only individuals with cognitive or visual impairments but also users navigating the site on mobile devices or those with limited internet bandwidth.
Descriptive images, accompanied by alt text, not only make visual content accessible to individuals with visual impairments but also provide context and clarity for all users. By conveying information through both visual and textual means, websites become more comprehensible and engaging for everyone.
Readable text, with appropriate font sizes, contrast ratios, and spacing, ensures legibility across various devices and screen sizes. This is particularly beneficial for users with visual impairments or reading difficulties, but it also enhances readability for users in different contexts, such as reading on small screens or in low-light environments.
Moreover, accessible design practices often lead to cleaner and more streamlined interfaces, reducing clutter and cognitive load for all users. By prioritizing usability and clarity, accessible websites foster a positive user experience that resonates with a broad audience, regardless of their abilities or technological proficiency.
In essence, the principles of website accessibility align closely with those of user-centered design, emphasizing usability, clarity, and inclusivity. By embracing these principles, organizations not only fulfill their legal and ethical obligations but also unlock the full potential of their digital platforms to deliver exceptional user experiences for everyone.
Broader Audience Reach
Making websites accessible opens doors to a vast and diverse audience, including individuals with disabilities who often face exclusion from online spaces. By ensuring that websites are usable for everyone, businesses and organizations can tap into new markets and connect with a broader demographic. Moreover, accessible websites foster a sense of inclusivity and respect, sending a powerful message that all customers are valued and welcome.

The benefits of reaching a larger audience extend beyond mere numbers. Increased engagement stems from the fact that accessible websites are easier to use and navigate, leading to longer sessions and more interactions with content. When individuals with disabilities can access information and services without barriers, they are more likely to engage with a website’s offerings, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or participating in online communities.
Furthermore, the satisfaction derived from a positive online experience translates into heightened customer loyalty. When individuals feel valued and supported by a brand, they are more inclined to return for future transactions and recommend the business to others. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses not only cultivate strong customer relationships but also differentiate themselves as socially responsible entities that prioritize inclusivity and equity.
Beyond direct financial returns, there are also intangible benefits to consider. A reputation for accessibility can enhance a company’s brand image, positioning it as a leader in diversity and inclusion. This positive association resonates with customers and can influence their perception of the brand’s values and integrity. In an increasingly competitive marketplace, where consumers actively seek out brands that align with their beliefs, accessibility can serve as a powerful differentiator that sets businesses apart from their competitors.
The impact of website accessibility goes far beyond compliance—it is a strategic imperative that drives business growth, fosters customer loyalty, and enhances brand reputation. By embracing accessibility as a core value, businesses and organizations can unlock the full potential of their online presence and create meaningful connections with diverse audiences, leading to sustained success in the digital landscape.
SEO Benefits
The intersection between website accessibility and search engine optimization (SEO) represents a powerful synergy that can significantly enhance a website’s online visibility and reach. Many accessibility practices not only improve the user experience for individuals with disabilities but also align closely with SEO best practices, ultimately benefiting all users.
One key accessibility practice is providing descriptive alt text for images. Alt text serves as a textual alternative to images, providing context and information for users who may not be able to see them. From an SEO perspective, alt text provides valuable metadata that search engine crawlers use to understand the content of images and index them appropriately. By incorporating relevant keywords into alt text, websites can improve their chances of ranking higher in image search results, thereby increasing their visibility to potential visitors.

Similarly, creating well-structured content is a fundamental aspect of both accessibility and SEO. Clear and organized content not only makes it easier for individuals with disabilities to navigate and understand but also improves readability and comprehension for all users. Search engine algorithms prioritize websites with well-structured content, as it indicates a higher level of relevance and authority. By using headings, lists, and other formatting elements effectively, websites can improve their chances of ranking well in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Moreover, accessible websites tend to load faster and perform better across different devices and screen sizes, which are important factors for SEO. Search engines prioritize websites that offer a seamless user experience, including fast loading times and mobile responsiveness. By optimizing for accessibility, websites inherently optimize for these SEO factors, thereby improving their overall search engine rankings.
Furthermore, as search engines continue to evolve and prioritize user experience metrics, such as Core Web Vitals, accessibility will likely play an increasingly important role in SEO. Websites that prioritize accessibility demonstrate a commitment to providing an inclusive and user-friendly experience, which can positively impact their search engine rankings and overall online visibility.
In essence, the alignment between accessibility and SEO underscores the importance of considering both aspects in website development and optimization strategies. By embracing accessibility best practices, businesses and organizations not only improve the usability and inclusivity of their websites but also enhance their search engine visibility and attract a wider audience, ultimately driving greater success in the digital realm.
Social Responsibility
Prioritizing website accessibility is not just a technical consideration but a reflection of an organization’s values and commitment to social responsibility. By making their digital platforms accessible to individuals of all abilities, businesses and organizations send a powerful message about their dedication to diversity, inclusivity, and equal opportunities for all.
At its core, accessibility is about ensuring that everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities, can access and interact with online content. By investing in accessibility, organizations demonstrate empathy and consideration for individuals with disabilities, recognizing their right to participate fully in the digital world. This commitment to inclusivity extends beyond legal obligations and reflects a genuine desire to create a more equitable and accessible society.

Prioritizing website accessibility also aligns with broader ethical business practices. It signifies a willingness to go above and beyond minimum requirements to ensure that all stakeholders are considered and respected. In an increasingly interconnected and diverse world, businesses that prioritize accessibility are viewed as ethical leaders, setting a positive example for others to follow.
Furthermore, accessible websites have the potential to positively impact society at large by breaking down barriers and fostering greater inclusion. When individuals with disabilities can access information, services, and opportunities online, they are better equipped to participate in education, employment, and social interactions. This not only benefits individuals with disabilities but enriches society as a whole by tapping into a diverse range of talents, perspectives, and experiences.
From a branding and reputation standpoint, prioritizing website accessibility can enhance an organization’s image and credibility. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the values and practices of the companies they support, and accessibility is becoming an important factor in shaping brand perception. Organizations that demonstrate a genuine commitment to accessibility are more likely to earn the trust and loyalty of customers, employees, and partners who share those values.
In summary, prioritizing website accessibility is not just a technical necessity but a reflection of an organization’s values and commitment to social responsibility. By embracing accessibility, businesses and organizations signal their dedication to diversity, inclusivity, and equal opportunities, thereby contributing to a more inclusive and equitable society.
What Are The Different Accessibility Features You Can Implement On Your Website
Implementing accessibility features on a website involves addressing various aspects of design, functionality, and content to ensure that users with disabilities can access and interact with the site effectively. Here are some key accessibility features that you can implement:
1. Alternative Text (Alt Text) for Images
Providing descriptive alt text for images enables individuals who use screen readers to understand the content and context of images on the website.
2. Semantic HTML
Using proper HTML markup and semantic elements helps screen readers and other assistive technologies interpret and navigate the content more accurately.
3. Keyboard Accessibility
Ensuring that all functionality and interactive elements can be accessed and operated using only a keyboard is essential for users who cannot use a mouse.
4. Focus Indicators
Clearly visible focus indicators help users understand where they are on the page when navigating using a keyboard, improving usability for keyboard-only users.
5. Captioned Media
Providing captions for videos and other multimedia content ensures that individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing can access the audio information.
6. Transcripts and Audio Descriptions
Offering transcripts for audio content and audio descriptions for visual content enables users with disabilities to access information through alternative means.
7. Readable Text
Using clear and legible fonts, appropriate font sizes, and sufficient color contrast enhances readability for users with visual impairments or reading difficulties.
8. Responsive Design
Ensuring that the website is responsive and adapts to different screen sizes and devices benefits users with varying abilities and preferences.
9. Accessible Forms
Designing forms with clear labels, logical tab order, and proper error handling helps users with disabilities complete tasks and provide information without barriers.
10. Skip Navigation Links
Including skip navigation links allows users to bypass repetitive navigation menus and quickly access the main content of the page, improving efficiency for screen reader users.
11. Aria Roles and Attributes
Using ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and attributes appropriately enhances the accessibility of dynamic and interactive content for screen reader users.
12. Text-to-Speech Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility with text-to-speech software enables users with visual impairments to have the content read aloud to them.
13. Accessible Color Choices
Avoiding reliance on color alone to convey information and ensuring sufficient color contrast supports users with color blindness or low vision.
14. Consistent and Predictable Layout
Maintaining a consistent and predictable layout across pages helps users with cognitive disabilities navigate and understand the structure of the website.
15. Testing and User Feedback
Regularly testing the website with assistive technologies and gathering feedback from users with disabilities can help identify accessibility issues and improve the user experience.
By incorporating these accessibility features into your website design and development process, you can create a more inclusive and user-friendly experience for all visitors, regardless of their abilities or assistive technology usage.
What Are Some Tools To Check Website Accessibility?
There are several tools available to help check website accessibility and identify potential issues that may hinder users with disabilities from accessing and using the site effectively. Here are some popular tools:
1. WAVE
WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool) is a web accessibility evaluation tool provided by WebAIM. It allows you to enter a web page URL and generates a detailed accessibility report highlighting potential issues and providing suggestions for improvement.
2. Lighthouse
Lighthouse is an open-source tool developed by Google that is integrated into the Chrome browser’s DevTools. It includes an accessibility audit feature that evaluates web pages against a set of best practices and provides actionable recommendations for improving accessibility.
3. axe
axe is an accessibility testing tool provided by Deque Systems. It offers both browser extensions and command-line interfaces for running accessibility tests on web pages. axe provides detailed reports with prioritized issues and suggested fixes.
4. Siteimprove
Siteimprove is a comprehensive digital accessibility platform that offers automated scanning tools, manual accessibility checks, and ongoing monitoring of website accessibility compliance. It provides detailed reports and prioritized recommendations for addressing accessibility issues.
5. Pa11y
Pa11y is an open-source accessibility testing tool that can be used via a web interface, command-line interface, or integrated into automated testing workflows. It offers flexibility and customization options for running accessibility tests on web pages.
6. Tenon.io
Tenon.io is a cloud-based accessibility testing tool that provides automated scanning and reporting for web accessibility issues. It offers integration with development workflows and provides detailed insights into accessibility compliance.
7. Deque Axe Browser Extension
The Deque Axe browser extension is available for Chrome and Firefox and provides on-the-fly accessibility testing of web pages. It highlights accessibility issues directly within the browser and offers guidance on how to fix them.
8. Accessibility Insights
Accessibility Insights is a suite of tools provided by Microsoft for testing web accessibility. It includes browser extensions for Chrome and Edge, as well as desktop applications for Windows and macOS, offering various testing and diagnostic features.
These tools can help web developers, designers, and content creators ensure that their websites are accessible to all users and comply with relevant accessibility standards and guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). It’s important to note that while automated testing tools can identify many accessibility issues, manual testing and user feedback are also essential for thorough accessibility evaluation.
What Are Some Examples Of Accessible Websites?
Several websites demonstrate exemplary accessibility practices, setting a high standard for inclusivity and usability. Here are a few examples:
BBC
The BBC website is known for its commitment to accessibility, offering a wide range of features and tools to ensure that users of all abilities can access its content. The site provides keyboard navigation support, clear headings and labels, descriptive alt text for images, and adjustable font sizes and color contrast options. Additionally, the BBC offers accessibility help and support resources for users with disabilities.
Microsoft
Microsoft’s website is designed with accessibility in mind, featuring semantic HTML markup, ARIA landmarks, and keyboard navigation support. The site also provides accessible forms, captions for multimedia content, and options for adjusting text size and contrast. Microsoft offers accessibility features and resources across its products and services, demonstrating a commitment to inclusion and diversity.
Deque University
Deque University’s website is dedicated to providing accessible training and resources for web developers, designers, and content creators. The site itself serves as a model of accessibility best practices, with clear navigation, descriptive headings, and accessible forms. Deque University offers courses, tutorials, and certification programs focused on web accessibility, helping to educate and empower individuals to create more inclusive websites.
Gov.uk
The Gov.uk website, managed by the UK government, is renowned for its accessibility and user-centered design. The site prioritizes simplicity, clarity, and ease of use, with accessible navigation, plain language content, and responsive design. Gov.uk provides accessibility guidance and resources for government agencies and organizations, promoting accessibility across the public sector.
Apple
Apple’s website exemplifies accessibility through its intuitive design, clear navigation, and comprehensive accessibility features. The site offers keyboard navigation support, descriptive alt text for images, and captions for multimedia content. Apple also provides accessibility features and support for its products, ensuring that users with disabilities can fully utilize their devices and services.
These examples highlight the importance of integrating accessibility into website design and development processes, as well as the positive impact that accessible design practices can have on user experience and inclusivity. By following the lead of these accessible websites and prioritizing accessibility, organizations can create digital experiences that are welcoming and usable for users of all abilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, website accessibility is not just a legal requirement or a technical consideration—it’s a moral imperative and a reflection of our commitment to inclusivity, diversity, and equal opportunities for all individuals. By prioritizing accessibility in website design and development, businesses and organizations can create digital environments that are welcoming, usable, and empowering for users of all abilities.
From providing descriptive alt text for images to ensuring keyboard navigation support and offering adjustable font sizes, there are numerous accessibility features that can enhance the user experience and foster inclusivity. Moreover, accessible websites benefit not only individuals with disabilities but also all users, leading to increased engagement, customer satisfaction, and brand loyalty.
As we move forward, let us continue to advocate for accessibility, championing the principles of inclusion and equality in the digital realm and beyond. Together, we can create a more accessible and inclusive online world where everyone can participate fully and equally, regardless of their abilities or differences.